A ball of mass 0.220 kg that is moving – A ball of mass 0.220 kg in motion exhibits a fascinating interplay of kinematics, dynamics, energy, and rotational motion. Understanding the intricate relationships between these concepts unveils the fundamental principles governing the behavior of moving objects.
As the ball traverses space, its kinematics describes the geometric aspects of its motion, including displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Dynamics delves into the forces acting upon the ball, such as gravity and friction, and their influence on its momentum. Energy transformations, including kinetic and potential energy, accompany the ball’s motion, providing insights into its work-energy relationship.
Kinematics
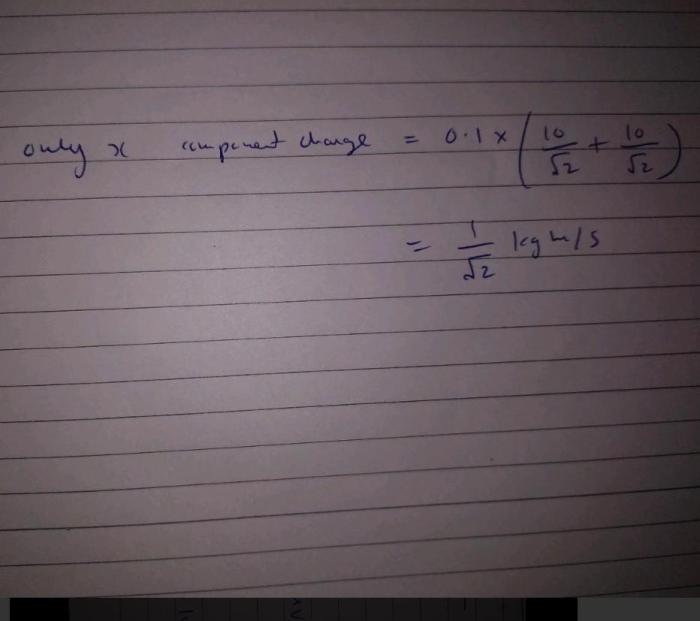
Kinematics is the branch of physics that describes the motion of objects without considering the forces that cause the motion. It is concerned with the mathematical description of the motion of a ball, including its position, velocity, and acceleration. The different types of motion that a ball can undergo include:
- Linear motion: The ball moves in a straight line.
- Projectile motion: The ball is launched into the air and follows a parabolic path.
- Circular motion: The ball moves in a circle.
The equations of motion are a set of mathematical equations that can be used to analyze the motion of a ball. These equations relate the position, velocity, and acceleration of the ball to the forces that are acting on it.
Dynamics

Dynamics is the branch of physics that describes the motion of objects by considering the forces that cause the motion. It is concerned with the relationship between the forces that act on a ball and its motion. The forces that act on a ball in motion include:
- Gravity: The force of gravity pulls the ball towards the ground.
- Air resistance: The force of air resistance opposes the motion of the ball.
- Friction: The force of friction opposes the motion of the ball when it is in contact with a surface.
Momentum is a measure of the amount of motion that a ball has. It is defined as the product of the mass of the ball and its velocity. Momentum is a conserved quantity, which means that it cannot be created or destroyed.
The concept of momentum can be used to analyze the motion of a ball by considering the changes in its momentum over time.
Energy: A Ball Of Mass 0.220 Kg That Is Moving
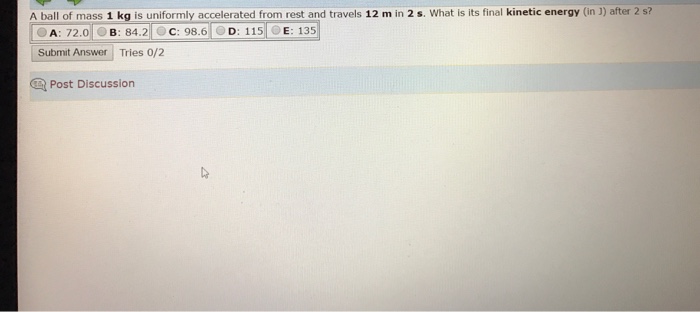
Energy is the ability to do work. It is a conserved quantity, which means that it cannot be created or destroyed. The different forms of energy that a ball can have include:
- Kinetic energy: The energy of motion.
- Potential energy: The energy of position.
- Thermal energy: The energy of heat.
Energy transformations occur when a ball is in motion. For example, when a ball is thrown into the air, its kinetic energy is converted into potential energy as it rises. When the ball falls back to the ground, its potential energy is converted back into kinetic energy.
The work-energy theorem is a theorem that relates the work done on a ball to its change in energy. The work-energy theorem can be used to analyze the motion of a ball by considering the changes in its energy over time.
Rotational Motion
Rotational motion is the motion of an object around an axis. It is concerned with the mathematical description of the rotation of a ball, including its angular position, angular velocity, and angular acceleration. The different types of rotational motion that a ball can undergo include:
- Uniform circular motion: The ball rotates at a constant angular velocity.
- Non-uniform circular motion: The ball rotates at a variable angular velocity.
- Rolling motion: The ball rolls on a surface.
The equations of rotational motion are a set of mathematical equations that can be used to analyze the rotational motion of a ball. These equations relate the angular position, angular velocity, and angular acceleration of the ball to the forces that are acting on it.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of mass in the context of a moving ball?
Mass plays a crucial role in determining the ball’s inertia, which resists changes in its motion. A higher mass implies greater inertia, making the ball more difficult to accelerate or decelerate.
How does gravity affect the motion of a ball?
Gravity exerts a downward force on the ball, causing it to accelerate towards the ground. This force influences the ball’s trajectory and velocity.
What is the relationship between kinetic energy and the motion of a ball?
Kinetic energy represents the energy of motion. As the ball moves, its kinetic energy increases пропорционально to the square of its velocity.

