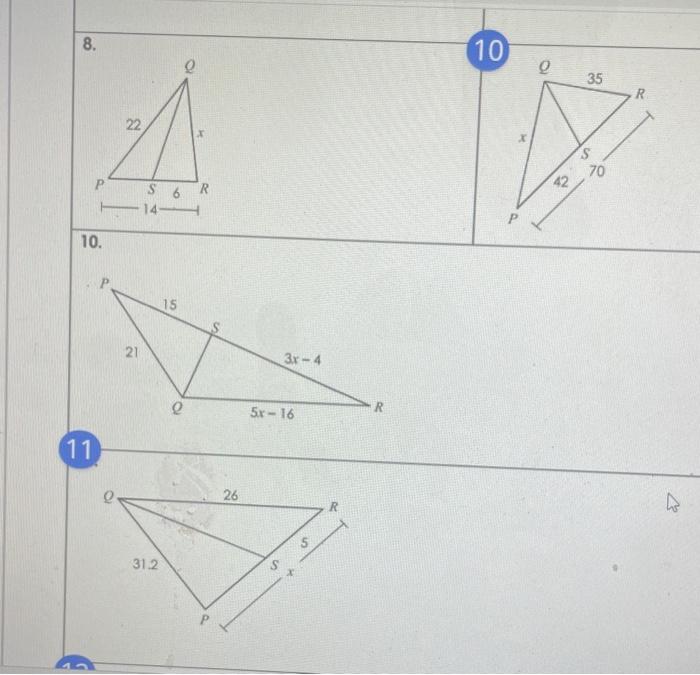
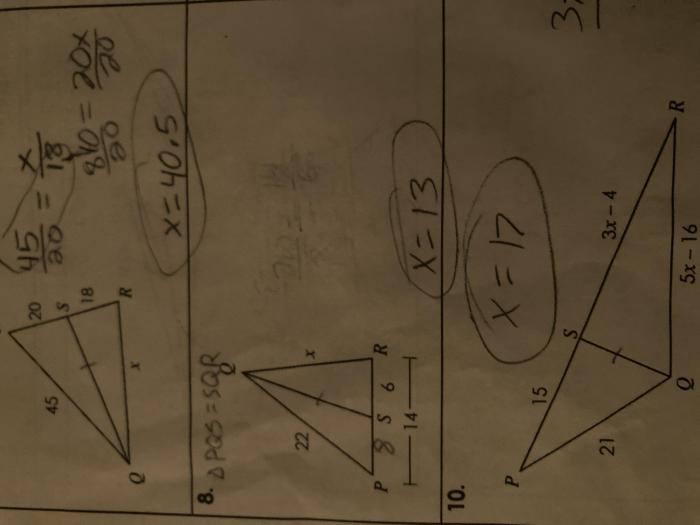
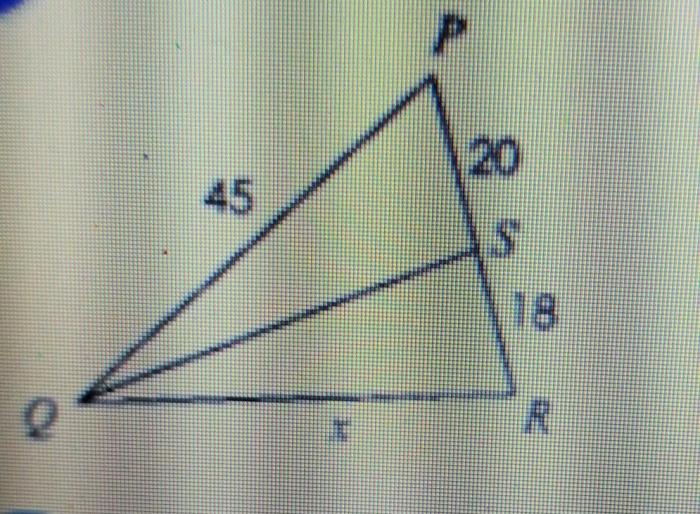
If qs represents an angle bisector solve for x – Embarking on an exploration of angle bisectors and their pivotal role in determining unknown side lengths, this discourse delves into the intricacies of the theorem that connects angle bisectors to side lengths. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of triangles and their geometric relationships.
Angle bisectors, the pivotal lines that divide angles into congruent halves, hold the key to unlocking the secrets of triangle geometry. Their properties and the theorem that governs their relationship with side lengths empower us to solve for unknown side lengths with precision.
Definition of Angle Bisector: If Qs Represents An Angle Bisector Solve For X
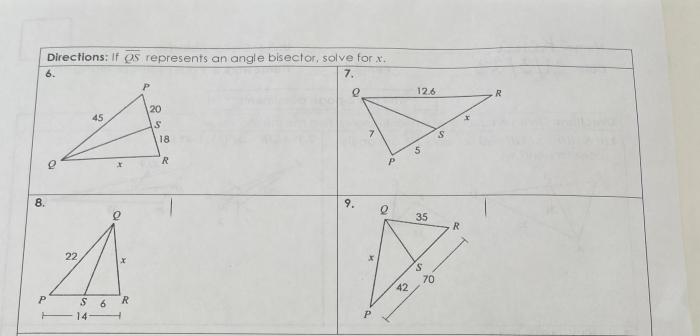
An angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle into two equal parts. It passes through the vertex of the angle and lies in the interior of the angle. The two rays that form the angle bisector are called the sides of the angle bisector.
Angle bisectors have several important properties:
- The angle bisector of an angle is perpendicular to the line segment connecting the two sides of the angle.
- The angle bisector of an angle divides the opposite side of the angle into two segments that are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides.
- The angle bisector of an angle is the only line that passes through the vertex of the angle and divides it into two equal parts.
Theorem Relating Angle Bisector and Side Lengths
The theorem relating an angle bisector to the lengths of the sides of a triangle states that:
If a ray bisects an angle of a triangle, then the ratio of the lengths of the sides of the triangle that form the angle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the segments of the third side formed by the angle bisector.
In other words, if we have a triangle with sides a, b, and c, and the angle bisector of angle A divides side c into segments x and y, then:
a/b = x/y
This theorem can be proven using similar triangles.
Here is an example to illustrate the theorem:
In triangle ABC, the angle bisector of angle A divides side BC into segments x and y. If AB = 6 cm, AC = 8 cm, and BC = 10 cm, then:
6/8 = x/y
Solving for x, we get:
x = 3 cm
And solving for y, we get:
y = 5 cm
Using the Theorem to Solve for Unknown Side Lengths
The theorem relating angle bisector and side lengths can be used to solve for unknown side lengths in a triangle when the angle bisector is known.
Here are the steps on how to solve for unknown side lengths using the theorem:
- Draw a diagram of the triangle and label the given information.
- Find the ratio of the lengths of the sides of the triangle that form the angle.
- Use the theorem to set up an equation relating the lengths of the sides of the triangle and the segments of the third side formed by the angle bisector.
- Solve the equation for the unknown side length.
Here is an example to illustrate the steps:
In triangle ABC, the angle bisector of angle A divides side BC into segments x and y. If AB = 6 cm, AC = 8 cm, and x = 3 cm, then:
The ratio of the lengths of the sides of the triangle that form the angle is 6/8 = 3/4.
Using the theorem, we can set up the following equation:
3/4 = 3/y
Solving for y, we get:
y = 4 cm
Therefore, BC = x + y = 3 cm + 4 cm = 7 cm.
Applications of the Theorem, If qs represents an angle bisector solve for x
The theorem relating angle bisector and side lengths has several applications in geometry and other fields.
Here are some examples of how the theorem is used in practice:
- In architecture, the theorem can be used to find the lengths of roof rafters and other structural elements.
- In surveying, the theorem can be used to find the distances between objects.
- In navigation, the theorem can be used to find the shortest distance between two points on a map.
Q&A
What is an angle bisector?
An angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles.
How can I use the angle bisector theorem to solve for unknown side lengths?
The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the lengths of the two segments created by an angle bisector is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the opposite sides of the triangle.
What are some real-world applications of the angle bisector theorem?
The angle bisector theorem can be used to solve problems in architecture, engineering, and design, such as determining the height of a building or the length of a bridge.