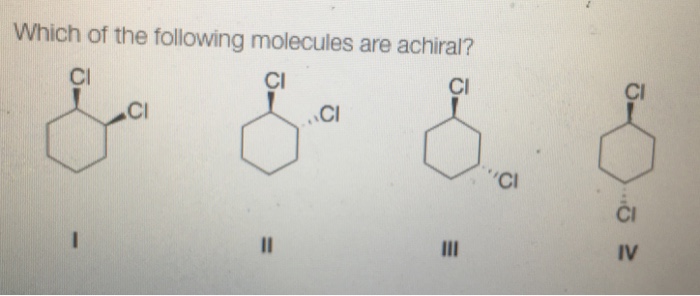
Chirality, a fundamental concept in chemistry, plays a crucial role in various fields, including drug development and material science. In this article, we delve into the intriguing realm of achiral molecules, exploring their unique characteristics and applications. Which of the following molecules is achiral? Join us on a journey to discover the answers.
The concept of chirality revolves around the handedness of molecules, where chiral molecules exist in two non-superimposable mirror-image forms. Achiral molecules, on the other hand, lack this handedness and are superimposable on their mirror images.
Definition of Chirality
Chirality is a fundamental concept in chemistry that refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule. A chiral molecule is one that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image, similar to the relationship between our left and right hands.
Chirality plays a crucial role in various fields, including pharmacology, drug development, and materials science.
Examples of chiral molecules include amino acids, sugars, and many pharmaceuticals. In contrast, molecules like methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are achiral due to their symmetrical structures.
Factors Determining Chirality
Chiral Centers
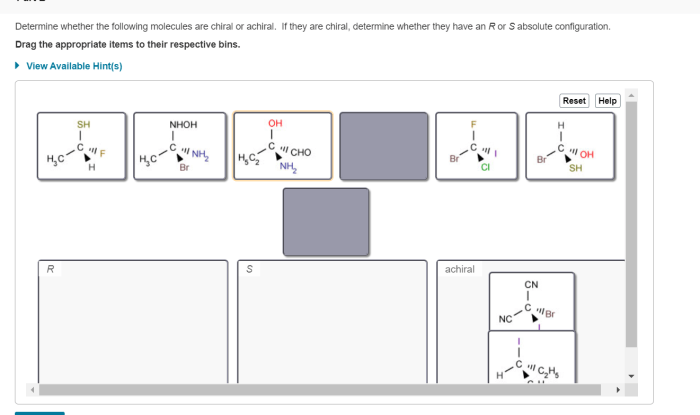
The presence of one or more chiral centers, also known as stereogenic centers, is a key factor in determining the chirality of a molecule. A chiral center is an atom that is bonded to four different groups or atoms, giving rise to two distinct spatial arrangements that are mirror images of each other.
Symmetry and Mirror Planes
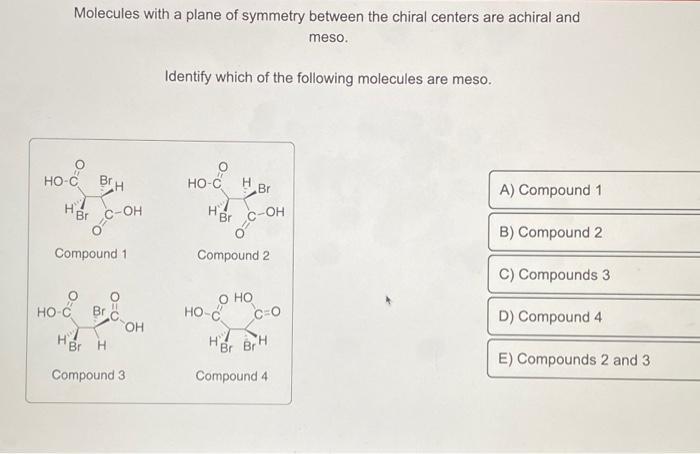
Molecules with a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry are achiral. A plane of symmetry is an imaginary plane that divides the molecule into two mirror-image halves. A center of symmetry is a point within the molecule where all equivalent points are equidistant from it.
Identification of Achiral Molecules
To identify achiral molecules, one can examine their symmetry. Molecules with any of the following properties are achiral:
- A plane of symmetry
- A center of symmetry
- Two or more identical chiral centers that cancel each other’s chirality
Examples of Achiral Molecules
Simple Achiral Molecules
- Methane (CH4)
- Ethane (C2H6)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Complex Achiral Molecules
- Benzene (C6H6)
- Naphthalene (C10H8)
- Cubane (C8H8)
Applications of Achirality: Which Of The Following Molecules Is Achiral
Drug Development and Pharmacology
Chirality plays a significant role in drug development and pharmacology. Many biological molecules, such as proteins and enzymes, are chiral. The different enantiomers of a chiral drug can have different biological activities, including efficacy and toxicity. Understanding the chirality of drugs is essential for optimizing their therapeutic effects and minimizing side effects.
Non-Chiral Materials, Which of the following molecules is achiral
Achiral molecules can serve as building blocks for non-chiral materials with unique properties. For example, achiral polymers can exhibit high strength and thermal stability, making them valuable for applications in engineering and aerospace.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of chirality in drug development?
Chirality is crucial in drug development as it affects the biological activity and efficacy of drugs. Enantiomers, mirror-image forms of chiral drugs, can have different interactions with biological targets, leading to varying therapeutic effects and side profiles.
How can achiral molecules be utilized in material science?
Achiral molecules serve as building blocks for non-chiral materials with specific properties. These materials find applications in optics, electronics, and other fields where chirality is undesirable.