Correctly identify all organs depicted in the diagram below – Correctly identifying all organs depicted in the diagram below is crucial for understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body. This guide will provide a detailed description of each organ, its function, and its significance to the overall system, empowering readers with the knowledge to accurately interpret anatomical diagrams.
The following paragraphs will delve into the intricacies of the organs depicted, exploring their structure, function, and interrelationships. By organizing the information in a clear and concise manner, this guide aims to enhance comprehension and facilitate the acquisition of essential knowledge.
Identify Organs: Correctly Identify All Organs Depicted In The Diagram Below
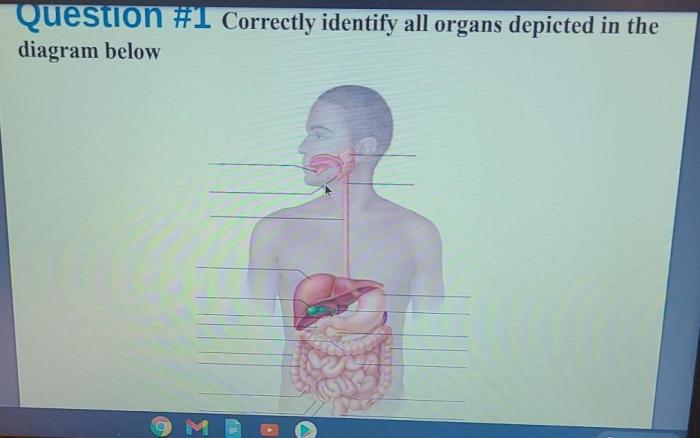
The diagram depicts several essential organs within the human body. Each organ plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Let’s explore each organ in detail:
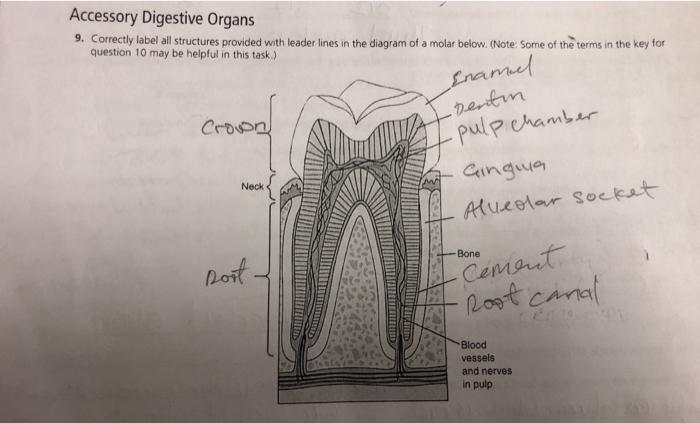
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It consists of four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). The heart’s function is to circulate oxygenated blood to the body’s tissues and remove deoxygenated blood for re-oxygenation.
Lungs
The lungs are paired organs located in the chest cavity. They facilitate gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be exhaled. The lungs consist of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which increase the surface area for efficient gas exchange.
Liver
The liver is the largest internal organ, located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. It performs over 500 vital functions, including filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile for digestion, and storing energy as glycogen.
Kidneys
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine. They filter waste products from the blood, regulate blood pressure, and maintain electrolyte balance. The kidneys also produce urine, which carries waste products out of the body.
Stomach, Correctly identify all organs depicted in the diagram below
The stomach is a muscular organ located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. It secretes gastric juices that break down food into smaller molecules, facilitating digestion. The stomach also stores food temporarily before releasing it into the small intestine for further digestion and absorption.
Small Intestine
The small intestine is a long, coiled tube located in the abdomen. It is responsible for the majority of nutrient absorption. The small intestine consists of three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Each section has specialized functions in the digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Large Intestine
The large intestine is a shorter, wider tube that continues from the small intestine. Its primary function is to absorb water and electrolytes from undigested food, forming feces. The large intestine also contains beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion and immune function.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key features to consider when identifying organs in a diagram?
Shape, size, location, and relationship to other organs are crucial factors for accurate identification.
How can I improve my ability to interpret anatomical diagrams?
Practice, studying labeled diagrams, and understanding the anatomical terminology can enhance your interpretation skills.
What are the most common challenges in correctly identifying organs in a diagram?
Variations in organ appearance, overlapping structures, and lack of color can pose challenges.